Ever wondered how a tiny glucose meter could play a big role in your daily health routine? Whether you’re managing diabetes or just curious about your blood sugar levels, this little device does more than you think. From quick glucose test results to user-friendly designs that fit in your pocket, today’s meters are smarter, faster, and easier to use than ever. Let’s explore how this powerful tool can help you stay in control, feel better, and live smarter, one drop of blood at a time!
Blood Glucose Meter Overview
A blood glucose meter is a handheld device that helps people with diabetes measure blood glucose levels accurately. This glucose monitor provides quick glucose results using a small drop of blood, typically from the fingertip. Monitoring blood sugar regularly supports diabetes management and helps prevent complications. Various blood glucose monitoring devices offer features tailored to specific needs, including large displays for visually impaired users and smartphone app connectivity. Recommended by your health care provider, these meters play a vital role in diabetes care and control.
What Is a Blood Glucose Meter?
A blood glucose meter is a compact device designed for home use to measure blood sugar levels easily. It works by analyzing a blood sample applied to a test strip, providing a glucose reading within seconds. Using a blood glucose meter allows adults with diabetes to check blood sugar frequently, which helps manage their diabetes more effectively. The American Diabetes Association recommends regular glucose tests as part of a diabetes care plan. Additionally, some meters include special features to make testing less painful and more user-friendly.
Did you know some glucose monitors connect to your smartphone and track your data automatically?
How Does a Glucose Monitor Work?
A glucose monitor measures glucose levels in a blood drop, usually collected by pricking your fingertip with a lancet or lancing device. The meter and test strips contain enzymes that react with the glucose in the blood, generating an electrical signal. This signal converts into a glucose reading displayed on the device screen. For accurate blood results, it is crucial to wash your hands before testing and use control solution to check meter accuracy regularly. Continuous glucose monitors (CGM) offer an alternative by measuring glucose levels continuously through a sensor, providing more data to manage diabetes.
Types of Blood Glucose Monitoring Devices
Blood glucose monitoring devices vary from basic meters to advanced continuous glucose monitors (CGM). Traditional blood glucose meters require a blood glucose test using a test strip and lancet. In contrast, CGM devices measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid without repeated finger pricks. Meters like Contour Next offer reliable glucose results and user-friendly features such as a large display and time and date stamps. Choosing the right device depends on your specific needs, including ease of use, accuracy, and integration with your diabetes treatment plan.
Read also Top Theft Alarm Systems
Using Test Strips and Lancets
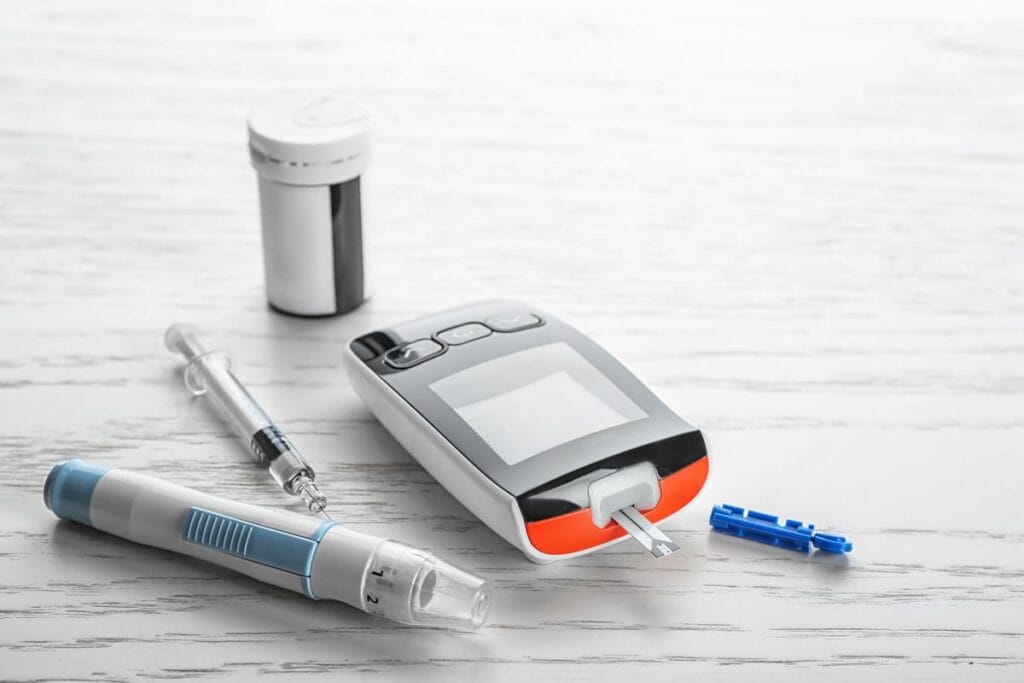
Test strips are vital components of blood glucose monitoring systems, as they react chemically with blood sugar to produce a readable glucose result. Proper storage of test strips ensures accurate blood glucose levels. Selecting the right lancet and lancing device can reduce pain and improve blood sample collection. Most people prick their fingertip, but alternative sites like the upper arm may be less painful for some users. Using lancets correctly helps avoid infection and ensures enough blood for testing.
Did you know the first glucose meter was invented in 1962 and weighed over a pound?
Understanding Test Strips Function
Test strips contain enzymes that react with the blood glucose on the strip, creating an electrical signal proportional to the glucose concentration. This reaction allows the glucose meter to display a glucose reading quickly. Using expired or improperly stored test strips may lead to less accurate results. Therefore, it is important to follow the user guide to maintain reliable blood glucose testing.
Choosing the Right Lancet and Lancing Device
The lancet is a small needle used to lance the skin and obtain a blood drop. Choosing a lancet with the right gauge and a lancing device that offers adjustable depth can minimize pain during blood sampling. Some meters offer less painful lancing devices recommended by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Using a proper lancet helps people with diabetes perform frequent blood sugar tests comfortably and safely.
How to Properly Lance Your Finger
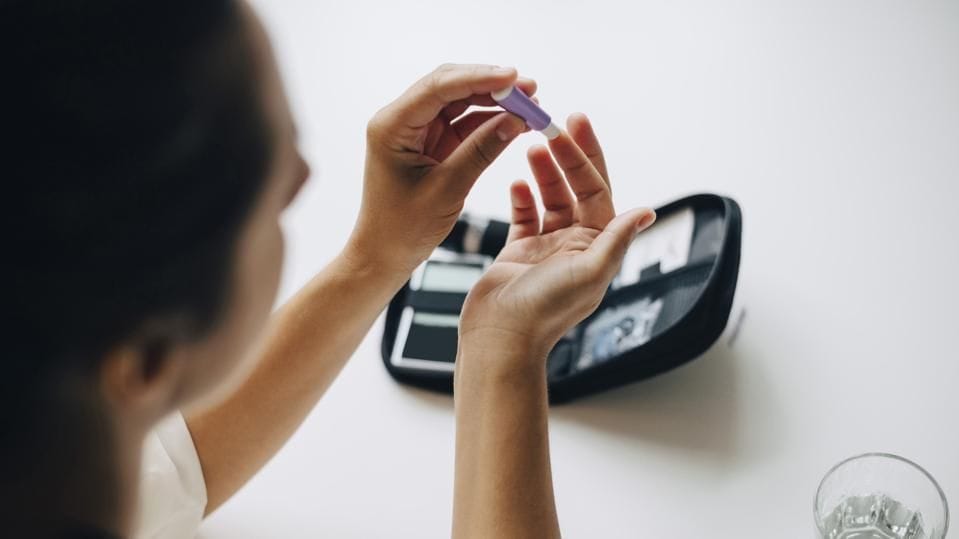
To get an accurate blood glucose test, wash your hands thoroughly before using the lancet. Prick the side of your fingertip rather than the pad to reduce discomfort. After lancing, gently squeeze to get a drop of blood, then apply it to the test strip immediately. Avoid excessive squeezing, which can dilute the sample with tissue fluid, leading to inaccurate glucose results. Proper lancing technique supports effective blood glucose monitoring at home.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels at Home
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes and preventing hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Using a meter kit designed for home use, people with diabetes can check blood sugar conveniently. Accurate blood glucose readings help guide treatment decisions and diet adjustments. Checking your blood sugar at consistent times, such as before meals and bedtime, improves diabetes care. Recording glucose readings assists your care team in adjusting your treatment plan effectively.
Did you know people without diabetes sometimes use CGMs to monitor diet and fitness?
Steps for Checking Your Blood Sugar
Start by washing your hands to ensure no contaminants affect the blood glucose test. Prepare your glucose meter, insert a test strip, and use the lancet to prick your fingertip. Apply the drop of blood to the test strip and wait for the meter to display your glucose results. Follow the instructions in your user guide carefully for accurate blood glucose testing. Regular blood sugar tests enable better diabetes management.
Interpreting Glucose Results Accurately
Blood glucose readings indicate the amount of sugar in your blood at the test time. Understanding whether your blood sugar level is low, normal, or high is critical. Factors to consider include food intake, medication, and physical activity, which can all affect glucose levels. Your healthcare provider will help you interpret glucose results in the context of your diabetes care. Maintaining blood glucose within the target range reduces the risk of complications.
Read about Radiofrequency Skin Treatment
Using the Meter Kit for Home Use
A meter kit usually includes the glucose meter, test strips, lancets, a lancing device, and control solution. The control solution helps verify that the meter and test strips work correctly, ensuring accurate blood glucose monitoring. For home use, it is important to store the kit components properly and replace consumables regularly. The meter kit empowers people with diabetes to manage their condition confidently and safely.
Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems

A blood glucose monitoring system integrates the glucose meter, test strips, lancets, and sometimes software or smartphone apps for data tracking. These systems facilitate monitoring blood glucose conveniently and effectively. Selecting a reliable blood glucose monitoring system ensures accurate glucose tests, essential for diabetes management. Some systems, like Contour Next, include advanced features to help users manage their glucose levels better.
Components of a Blood Glucose Monitoring System
The main components include the blood glucose meter, test strips, lancets, and a lancing device. Each part plays a role in obtaining an accurate blood glucose test. The meter analyzes the blood sample on the test strip and provides a glucose reading. Control solutions are also part of the system, used to verify meter accuracy periodically. Together, these components form a comprehensive blood glucose monitoring system.
Role of Control Solution in Accuracy
Control solution contains a known amount of glucose to test whether your blood glucose meter and test strips provide accurate readings. Using control solution regularly helps detect any errors or problems with the device. It ensures your blood glucose tests remain reliable, which is vital for managing diabetes. The American Diabetes Association advises routine control solution testing as part of diabetes care.
Features of Contour Next Blood Glucose Meters
Contour Next meters offer high accuracy, fast glucose results, and easy-to-read large displays. They support time and date stamping of glucose tests, which helps track blood sugar trends. Many meters offer smartphone app connectivity for better data management and sharing with your healthcare provider. These meters also feature less painful lancet options and are FDA certified for quality and safety.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar Testing
Regular blood sugar testing is crucial for people with diabetes to manage their condition effectively. Blood glucose tests help monitor how treatment plans impact glucose levels. Understanding the relationship between hemoglobin A1c (A1C) and blood sugar provides insight into average blood glucose over time. Managing blood sugar reduces risks of diabetes complications and improves quality of life.
Why Regular Blood Sugar Tests Matter in Diabetes
Checking your blood sugar regularly enables timely adjustments to medication, diet, or activity. It helps detect episodes of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia early. Frequent glucose monitoring is part of comprehensive diabetes management recommended by health care providers and diabetes organizations. It empowers people with diabetes to take control of their health.
Relationship Between Hemoglobin and Blood Glucose
Hemoglobin A1c measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, reflecting average blood glucose over 2–3 months. This test complements daily blood glucose monitoring by showing long-term glucose control. Maintaining a target A1C level reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications. Combining glucose tests with A1C provides a complete picture of diabetes care.
Best Practices for Blood Sugar Test Timing
Testing blood sugar before meals, after meals, and at bedtime gives a full picture of glucose fluctuations. Some people also test during symptoms of low or high blood sugar. Timing blood glucose tests consistently helps identify patterns and guide treatment. Your healthcare provider will recommend the best schedule based on your treatment plan and lifestyle.
User Guidance and Maintenance
Proper use and maintenance of your blood glucose monitor ensure accurate readings and device longevity. Following the user guide helps prevent common errors such as using expired test strips or incorrect lancing technique. Cleaning your device regularly reduces contamination risk. Addressing error codes promptly keeps your blood glucose monitoring reliable.
How to Use Your Blood Glucose Monitor Correctly
Begin by reading the user guide carefully to understand your device’s operation. Always use fresh test strips compatible with your glucose meter. Wash your hands before testing to avoid inaccurate blood glucose results. Follow each step, from inserting the test strip to applying blood and reading the glucose result, to ensure precision.
Cleaning and Maintaining Your Device
Keep your blood glucose monitor clean by wiping it with a damp cloth and avoiding harsh chemicals. Store the device and supplies in a dry, room-temperature environment. Replace lancets and test strips regularly as instructed. Proper maintenance supports accurate blood glucose monitoring and extends device life.
Troubleshooting Common Meter Issues
If your meter displays an error code, consult the user guide to identify the problem. Common issues include insufficient blood on the test strip, expired strips, or low battery. Contact your healthcare provider or the meter manufacturer for help if problems persist. Prompt troubleshooting ensures continuous and accurate blood glucose testing.
Frequently Asked Questions about Glucose Meter
Which device is best for measuring blood sugar?
The best device to measure blood depends on your needs. BGMs are reliable for most people with diabetes, while a CGM helps track how much glucose is in your body continuously. Some meters offer a smartphone app and large displays for the visually impaired, making checking your blood sugar easier. These tools can help you manage your diabetes more effectively by showing trends and average blood levels.
Do I need a prescription for a blood glucose monitor?
In most cases, you don’t need a prescription for a blood glucose monitor or blood sugar test kit. However, some advanced glucose test systems or CGM devices may require approval from a health care provider, especially for those without diabetes or seeking insurance coverage.
How can I check my blood sugar without a pricking finger?
You can avoid pricking your finger by using a CGM that measures glucose through a sensor on the skin. These systems are ideal for people with diabetes who want to avoid frequent fingersticks. Some glucose monitors scan the upper arm, making the process less painful and more convenient for home use.
Now that you’ve got the full scoop on glucose meters, it’s your turn! Have you picked the right device for your needs? Are you using all the features your meter offers? Whether you’re new to checking your blood sugar or a seasoned pro, there’s always something new to learn. Let us know what device you love and how it helps you manage your health!
Read also about Airsculpt Body Contouring Options